How Binary plan works ?
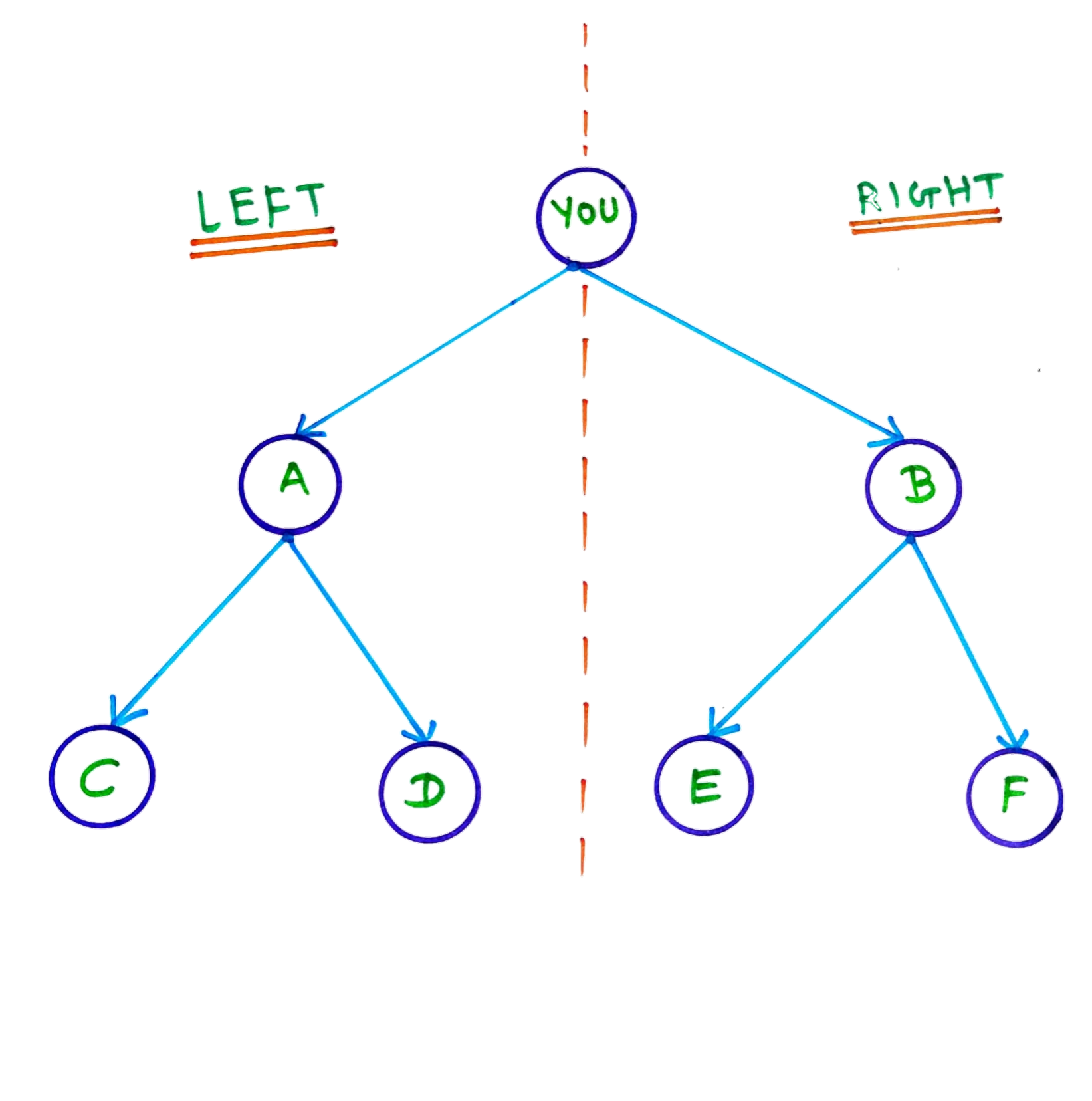
Binary plan is basically 2*n matrix plan with two legs (left leg and right leg) and unlimited depth where distributors can earn commission by balancing sales volume on both sides. There are different ratios for balancing sales volume on both sides; the famous ones are 1:1, 2:1 and 2:3. There are different terminologies in binary plan that one should know while choosing this business plan.
Spill Over
If Distributor refers more than 2 distributors, the new distributor will be added to the next available position in his/her network. This mechanism is known as spill over. The spillover actually boost team moral and promote team work in the network as everybody is getting benefited by new joining.
There are different types of spill over currently running in market :
-
Extreme Left or extreme Right Spillover
In this type of spillover distributors can place their referrals either extreme left side (left side of the left) or extreme right side (right side of the right) in their network. So they will be able to balance their sales volume by deciding which side to place their sponsors but same will not happen for their downlines. Refer fig.1.1
-
Custom Spillover
In this type of spillover distributors will have the choice to place their referrals wherever they want in their network. So they will be able to balance their sales volume as well as they can help their downlines to balance their sales volume too. Refer fig. 1.2
-
Balanced Spillover
In this type of spillover distributors will have to place their referrals on both sides one by one to balance their network. Distributors can decide to place this spill over on either their or their referral’s both sides one by one. Refer fig. 1.3
Capping
In Binary plan, Capping is a maximum amount distributor can earn in specific time period decided by the company. It is basically a limit set by MLM companies above which distributors cannot earn commissions. Capping can be in terms of cash or sales volume (pair matching). It helps company to regulate and manage their finances.
There are mainly two types of capping company uses.
-
Capping based on sales volume/pair matching
This capping is calculated based on the sales volume balanced by distributors on both sides. For example, if distributor has 250 PV sales a day on left side and 300 PV sales a day on right side, which means the matching is 250 PV. Now capping is set to 100 PV matching a day. Hence distributor will get commission for 100 PV matching only and the rest matched PV (150 PV) will be washed out. The Rest unmatched PV (50 PV) will either carry forward in next payment cycle or get washed out, whatever the company decides.
-
Capping based on commission
This capping is calculated based on binary matching income earned by distributors. For example, distributor is eligible for binary matching income of Rs 500/- per day. But if the company has capping of Rs 400/- per day for binary matching income, he/she will earn Rs 400/- only and the rest 100/- Rs will be washed out.
Trimming
In trimming every ‘X’ multiple of pair commission income will be trimmed or eliminated. For example, if company has decided to trim/eliminate pair commission for every 3rd pair, distributors won’t get pair commissions for 3rd pair, 6th pair, 9th Pair and so on.
Tail Binary
This is one of the trending concepts in binary plan these days. When 1st pair of distributor is completed in 2:1 or 1:2 ratio and all pairs after that are completed in 1:1 ratio, this technique is known as tail binary.
Types of incomes in Binary MLM Plan
-
Direct Sponsor Income
The Direct Sponsor income is also known as referral bonus.it is the benefit gained by a distributor for referring new distributors in his/her network. For example, company has decided to give distributors 7% of the direct sales they have made as a direct sponsor income.
-
Binary Matching Income
Binary matching income is also known as pair matching income. Distributors will earn either some percentage of matching sales volume on both sides or fixed amount on completion of a pair as binary matching income. For example, if distributor A has 400 PV on left side and 500 PV on right side, he/she will earn 10 % of 400 PV matching as binary matching income.
-
Sponsor Binary Income
Distributors will earn some percentage of binary matching income earned by their direct referral as a sponsor binary income. For example, company is giving its distributors 15% of their direct referral’s binary matching income as a sponsor binary income.
-
Rank based Royalty
Company puts aside some percentage of their turnover and distribute them equally among qualified rank holders based on their ranks. For example company is distributing 15% of their monthly turnover among silver rank holders. Now if company has 15 silver rank achievers this month so that 15% will be distributed equally among those silver rank holders. Every qualifier will get 1% of turnover as a royalty income.
-
Rewards
When distributor achieves milestones set by company within a specific time period (fixed or variable), they will get additional incentives as rewards. For example, company is giving additional 3% sponsor binary income if distributors complete 70 pairs within 60 days from their joining.
Advantages of Binary MLM Plan
-
Unlimited Depth : Unlike Uni-level plan, here distributors can earn commission for unlimited depth by balancing sales volume on both sides.
-
Spill Over : Distributors will get help form their up-line for building a network.
-
There is an opportunity for fast paced growth in terms of money and network.
-
Distributors have only two legs which make it easy to pay attention to their team and manage their business.
-
It is easily presentable plan as compared to Generation Plan.
Disadvantages of Binary MLM Plan
-
The biggest flaw of this plan is company has to distribute commissions whenever there is a pair matching regardless of company’s turnover.
-
Due to capping, distributor cannot earn more than certain amount despite of having deeper network.
-
In this plan, income calculation is very speculative and complex which create high possibility of making losses for company.
-
This plan is not suitable for multiple products with different percentage of margins.
.webp)
.webp)